In a world where every device from refrigerators to cars is becoming smarter and more interconnected, the Internet of Things (IoT) has transcended buzzword status to become a transformative force in technology and business. Beyond the convenience of controlling home appliances with a smartphone or monitoring industrial machinery remotely, IoT is ushering in a new era of investment opportunities.
In this article, we will chart the groundbreaking segments, emerging trends, and the leading private players within the IoT landscape.
Introduction to IoT
The IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices and systems that communicate and exchange data over the internet. Ranging from household appliances to industrial machinery, these use sensors and software to collect and share information, enabling automation, monitoring, and improved efficiency.
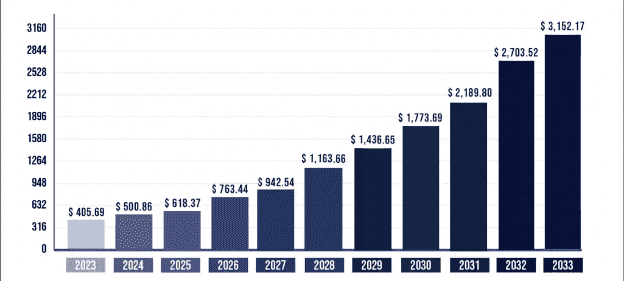
By 2033, the global IoT market is expected to reach approximately $3,152.17 billion (22.68% CAGR). This growth is driven by several key factors: the proliferation of connected devices, advancements in wireless communication technologies like 5G, and the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in IoT applications.
Key Growth Trends
Proliferation of Smart Devices - The number of IoT devices worldwide is forecast to almost double from 15.9 billion in 2023 to more than 32.1 billion in 2024.
5G Connectivity - The rollout of 5G networks accelerates IoT growth by providing faster data transfer, lower latency, and greater capacity, enhancing communication for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation.
Smart Cities - Urban areas are leveraging IoT to optimize infrastructure and services, including traffic management, energy use, waste management, and public safety, with significant investment driving market growth. The global smart cities market is expected to grow to over $2.4 trillion by 2027, driven by increasing IoT adoption.
Healthcare - IoT is transforming healthcare with remote patient monitoring, telemedicine, and connected medical devices, improving health monitoring, early diagnosis, and patient outcomes, especially for chronic diseases and elderly care.
AI and IoT Convergence - The convergence of AI and IoT drives enterprise investments, unlocking advanced analytics, predictive capabilities, and autonomous decision-making to improve operational efficiency and customer experiences.
Importance of the IoT sector
The IoT is having a significant and measurable impact across various industries and aspects of our lives. In terms of cost savings and efficiency improvements, IoT-enabled systems can reduce energy consumption by 5-15% through better monitoring and optimization. IoT in manufacturing can improve productivity by 10-20% and reduce machine downtime by 20-40%. Additionally, IoT in logistics and supply chain management can reduce costs by 10-40% through improved asset utilization and inventory management.
When it comes to revenue generation and new business models, IoT-enabled products and services can generate recurring revenue streams for companies. IoT also enables companies to develop new business models around product-as-a-service and servitization, driving additional revenue.
In the realm of improved health and safety, IoT wearables and remote monitoring devices can reduce healthcare costs by 15-20% through early detection and prevention of health issues. IoT sensors in industrial settings can also improve worker safety by monitoring conditions and alerting on potential hazards, reducing workplace injuries by 25% or more.
The impact of IoT on customer experience is also noteworthy. IoT-connected products allow companies to gather real-time usage data, leading to 10-40% improvements in customer satisfaction through better product development and personalization. IoT-enabled automation and convenience features, such as smart homes and connected cars, can improve customer experience and satisfaction by 15-30%.
Finally, IoT is also delivering environmental benefits. IoT-enabled smart grids and energy management systems can reduce electricity consumption by 1.8 PWh and fuel consumption by 3.5 PWh annually by 2030. IoT-powered waste management and recycling systems can also reduce waste by 10-30% through better monitoring and optimization.
Global Demand Drivers
Advancements in Connectivity - The rollout of 5G networks drives IoT adoption, especially in real-time applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation. Improvements in Wi-Fi and Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWANs) expand IoT device capabilities and deployment.
Growing Adoption of Smart Devices - The proliferation of smart home appliances, wearable fitness trackers, industrial sensors, and connected vehicles drives IoT demand. These devices offer enhanced convenience, efficiency, and remote monitoring for consumers and businesses.
Data Analytics - Advanced data analytics, including machine learning and AI, enable real-time analysis of IoT data for predictive maintenance, better decision-making, and optimized operations. This is valuable in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and energy.
Increasing Consumer and Business Demand - Both consumers and businesses are increasingly seeking connected solutions for convenience, efficiency, and productivity. This demand fuels the global growth of the IoT market.
Sustainability and Efficiency Goals - IoT technologies drive sustainability and energy efficiency by optimizing resource use, reducing waste, and supporting environmental monitoring. Examples include smart grids, smart meters, and IoT-enabled sustainable farming practices.
Investment Opportunities in IoT
Consumer IoT - This subset includes smart home devices like thermostats, lighting, and security systems that enhance automation and convenience, as well as wearables such as fitness trackers and smartwatches that monitor health and activity levels. It also encompasses connected vehicles with integrated internet access and advanced systems for navigation, diagnostics, and entertainment.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) - IoT in industrial settings focuses on manufacturing automation, using sensors and analytics to optimize processes and reduce downtime. It also includes predictive maintenance to anticipate equipment failures and schedule proactive maintenance, as well as supply chain optimization through real-time tracking and data analysis.
Healthcare IoT - This area leverages IoT for remote patient monitoring, where devices collect health data and transmit it to healthcare providers for continuous oversight. It also includes IoT-enabled medical devices like smart inhalers and insulin pumps, and health and fitness trackers that promote a healthy lifestyle by monitoring vital signs and physical activity.
Agricultural IoT - Smart farming technologies use IoT to monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. Field sensors collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and nutrients, while drones and precision equipment enable precise planting, spraying, and harvesting.
Smart Cities - IoT enhances urban living through intelligent transportation systems that improve traffic management, public transportation, and parking. It also includes smart energy grids for efficient energy distribution and management, and public safety and surveillance systems for crime prevention, emergency response, and environmental monitoring.
Retail IoT - This sub-sector focuses on inventory management through IoT solutions that track stock levels and manage supply chains efficiently. It also enhances customer experiences with personalized shopping through data analytics, and employs smart shelves and RFID tags for automated inventory tracking.
Building and Home Automation - IoT-enabled HVAC systems optimize energy use and comfort in buildings. Smart lighting systems adjust based on occupancy and natural light levels, while security and access systems enhance safety with smart locks, cameras, and alarms.
Energy and Utilities IoT - Smart meters provide real-time data on energy consumption, helping both consumers and utility providers. Energy management systems optimize energy use in buildings and industrial facilities, while grid monitoring and management technologies enhance the reliability and efficiency of power grids.
Emerging Trends and Areas of Growth
One of the key drivers is the late integration of generative AI, which is enhancing the capabilities of IoT solutions as a whole. By leveraging the vast amounts of data collected by IoT sensors, generative AI models can generate new insights and improve applications across industries - i.e., enhancing predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, synthetic data modeling, and energy optimization.
Another significant trend is the integration of emerging technologies like cloud computing, edge computing, and 5G into IoT platforms. This is fueling the growth of the IoT platform segment, as organizations seek effective solutions to connect IoT devices and enterprise applications. The enhanced data processing, improved connectivity, and advanced analytics capabilities enabled by these integrations are crucial for the expansion of IoT ecosystems.
However, it’s important to note that the rise in the number of connected IoT devices has also brought forth the challenge of cybersecurity and data privacy. Vulnerabilities in IoT device design and network connectivity could lead to data breaches and misuse, posing a potential barrier to further market expansion.
Strategic Insights for Investors
Key private players in the IoT industry include:
Nanit - An IoT startup that creates smart baby monitoring systems using computer vision and machine learning to track sleep patterns and provide insights. It has raised $74.6 million in Series C funding.
Detect Technologies - Uses AI and IoT devices to optimize operations, shutdowns, and turnarounds. It has handled over 50 global projects for companies like Shell and ExxonMobil and has raised $43.3 million in Series B funding.
Eight Sleep - Develops smart mattresses that track sleep patterns and provide temperature control. It has raised $162.1 million in Series C funding.
Risk Factors
As previously mentioned, IoT devices are highly susceptible to cyberattacks due to their interconnected nature and frequently inadequate security measures. These vulnerabilities make them prime targets for breaches that can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and result in significant financial losses.
Moreover, navigating regulatory landscapes proves challenging for the sector, as standards differ widely across regions. Ensuring compliance with diverse privacy laws, stringent data protection regulations, and specific industry mandates further complicates market entry and expansion efforts.
The IoT ecosystem, with its diverse players, technologies, and standards, also suffers from fragmentation. Issues with device and platform interoperability hinder the seamless integration and scalability of IoT solutions, requiring unified standards to improve efficiency and security.
Conclusion
Transformative technologies like 5G integration, edge computing, and AI applications are playing a big role in the future of the IoT. These advancements promise enhanced efficiency, real-time insights, and sustainable practices across diverse sectors. However, challenges such as cybersecurity risks, regulatory complexities, and market fragmentation underscore the need for vigilant risk management and innovation.
At Acquinox, we are dedicated to exploring these frontiers, providing deep insights and actionable strategies for navigating the complexities of IoT. We are committed to uncovering investment opportunities that harness the power of IoT to drive innovation, efficiency, and sustainable growth in the digital era.
Published by Samuel Hieber
