What if smartphones, smartwatches, and other smart devices could process data instantly, right where you are? It's the promise of edge computing. It's about bringing data processing closer to where it's needed, making everything faster and more efficient. For investors, edge computing is a fast-growing area with massive potential driven by advances in AI, 5G, and IoT.
In this article, we'll cut through the jargon to reveal the real opportunities in this exciting field. We'll explore what edge computing means for investors, highlight potential areas for growth, and show you why this technology could be the next big thing in the tech world.
Overview of Edge Computing
Edge computing is a technology approach that processes data closer to where it’s generated—at the "edge" of the network—rather than relying on a centralized cloud. The concept emerged in the late 1990s with content delivery networks, extending to mobile cloud computing ideas in the early 2000s. Throughout the 2010s, edge computing developed to support IoT, real-time processing, and low-latency applications. Today, it's widely adopted across industries, complementing cloud computing and enabling technologies like 5G, AI at the edge, and advanced IoT applications.
This industry has indeed grown rapidly, from an experimental technology to an essential tool for digital transformation. The global edge computing market is expected to reach $33.9 billion in 2024, and leap to $702.8 billion by 2033, representing a CAGR of nearly 40.0%, with industries such as manufacturing, telecommunications, healthcare and smart cities leading demand.
Growth Trends
- Real-Time Data Processing - Edge computing enables fast data processing on the spot, which is crucial in areas like autonomous vehicles and healthcare, where speed and responsiveness are essential.
- Enhanced IoT Applications - With more devices connected to the Internet of Things (IoT), edge computing is essential for handling the large amounts of data generated, especially in smart cities, homes, and industries.
- AI and Machine Learning at the Edge - Adding AI and machine learning to edge computing allows devices to make smart decisions quickly, helping with things like personalized services and predictive maintenance.
- 5G and Network Transformation - As 5G networks expand, edge computing can make use of the faster connections and lower delays, powering applications like AR, VR, and remote machinery control.
Why Edge Computing Matters
Edge computing is changing how we manage data, with uses in healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and more. For instance, in healthcare, edge computing supports real-time health monitoring and remote diagnostics, improving patient care. In manufacturing, it enables predictive maintenance and quality control, reducing downtime and increasing productivity. As tech companies and startups invest more in edge technology, the sector is expected to play a big role in our digital future.
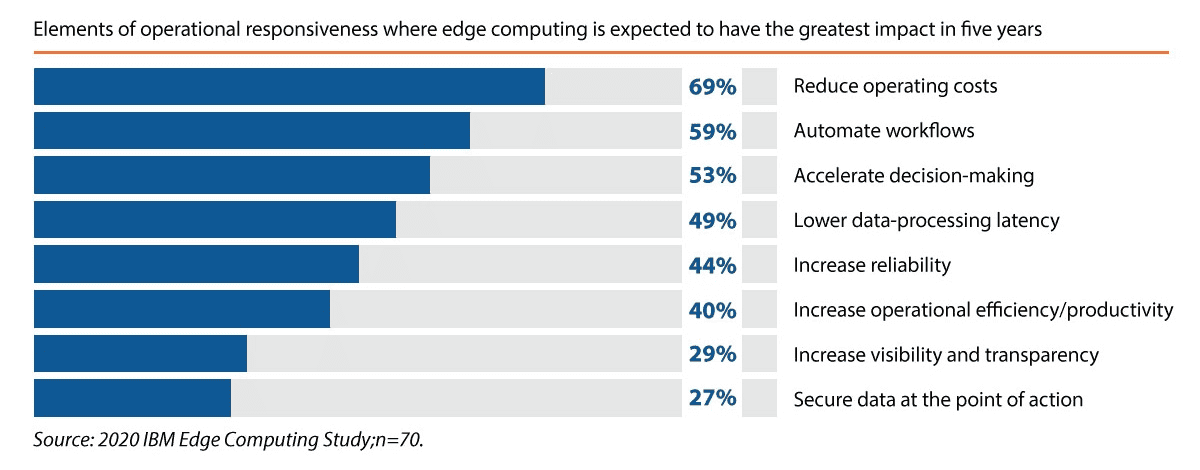
For investors, the demand for fast, local data processing offers many opportunities in sectors from healthcare to telecom. Edge computing’s flexibility is key to creating new business models and enhancing customer experiences.
Global Demand Drivers
- Low-Latency Needs - Applications like VR and autonomous driving require very low delays, achievable only with edge computing.
- IoT Growth - More connected devices mean more data, which needs to be processed locally to avoid overloading central systems.
- 5G Expansion - As 5G rolls out, edge computing can take advantage of its fast speeds and minimal lag times.
- Privacy and Security - Processing data closer to its source, especially for sensitive information, enhances data security, appealing to industries like finance and healthcare.
Sectors Poised for Disruption by Edge Computing
Edge computing is set to disrupt multiple sectors by enabling faster, more localized data processing and reducing reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure:
- Manufacturing - Edge computing enables real-time monitoring of production lines, predictive maintenance, and quality control. It allows for faster response times to equipment issues and optimizes overall production efficiency.
- Healthcare - In hospitals and clinics, edge computing enables real-time patient monitoring, fast processing of imaging data, and improved telemedicine. For instance, GE Healthcare’s Edison platform processes patient data on-site, accelerating diagnostics and enhancing data privacy by keeping information within the facility.
- Smart Cities - Edge computing powers various smart city applications, including traffic management, public safety systems, and environmental monitoring.
- Retail - Edge computing powers smart inventory management, personalized shopping experiences, and real-time analytics for customer behavior. It also enables cashier-less stores and advanced security systems.
- Energy and Utilities - Smart grids benefit from edge computing through improved energy distribution, real-time monitoring of power plants, and predictive maintenance of infrastructure.
- Agriculture - Precision farming techniques are enhanced by edge computing, enabling real-time monitoring of soil conditions, crop health, and livestock management.
- Telecommunications - With the rollout of 5G networks, edge computing is crucial for managing network traffic, reducing latency, and enabling new services.
- Finance and Banking - Edge computing enhances security for financial transactions, enables faster fraud detection, and improves the performance of high-frequency trading systems.
- Media and Entertainment - Content delivery networks benefit from edge computing, reducing latency for streaming services and enabling new augmented and virtual reality experiences.
Leading Edge Computing Technologies
- Edge AI - Integrating artificial intelligence directly at the edge, enabling real-time data processing, analysis, and decision-making without relying on cloud infrastructure.
- 5G-Enabled Edge Computing - Leveraging 5G networks to provide ultra-fast, low-latency connectivity for edge devices, significantly enhancing the capabilities and applications of edge computing.
- Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC) - Bringing cloud computing capabilities closer to the network edge, reducing latency and improving response times for time-sensitive applications.
- Blockchain in Edge Computing - Integrating blockchain technology to enhance security, transparency, and trust in edge computing environments.
- Fog Computing - Creating an intermediary layer between edge devices and the cloud to further optimize data processing and decision-making.
- Edge Computing for IoT - Enhancing IoT devices with edge computing capabilities for more efficient data handling and reduced reliance on cloud infrastructure.
- Software Containerization at the Edge - Utilizing containerization technologies to streamline application deployment and management in edge environments.
Strategic Insights for Investors
Investable Subsets in Edge Computing
- Edge Devices - These are the physical components, such as IoT sensors, cameras, smart appliances, and autonomous systems, that collect and sometimes pre-process data on-site. For example, NVIDIA’s Jetson devices are used in various applications requiring real-time processing, such as autonomous drones, robotics in warehouses, and medical imaging systems.
- Edge Infrastructure - This category includes the hardware and networks that support data processing at the edge, such as micro data centers, local servers, and edge-specific networking equipment. These infrastructure components are critical for delivering low-latency, high-availability data processing closer to end-users.
- Software Platforms - Edge software platforms provide the operating systems, frameworks, and tools that manage applications, coordinate data flows, and orchestrate edge devices and infrastructure. Examples include real-time analytics platforms, edge OS, and device management systems (mostly Linux based), which help streamline operations and ensure efficient data processing.
- Security Solutions - Protecting data at the edge is essential as data often moves between distributed devices and networks. Edge-specific security solutions offer encryption, intrusion detection, secure access controls, and threat intelligence to safeguard data integrity and privacy, especially critical in industries like healthcare, finance, and critical infrastructure.
Key Private Players
- EdgeConneX - EdgeConneX provides edge data centers that cater to content, network, cloud, and IT service providers, helping them deliver low-latency solutions to users at the edge of the network. With over $1.7 billion in funding, the company continues to expand its footprint in global edge computing markets, positioning itself as a critical infrastructure provider in both developed and emerging markets.
- Vapor IO - Vapor IO specializes in developing edge colocation and interconnection platforms, which combine multi-tenant colocation, software-defined interconnection, and high-speed networking to support low-latency workloads at the edge of wireless and wireline access networks. With $215 million in funding, the company is innovating the edge infrastructure ecosystem, with particular emphasis on supporting smart cities and autonomous vehicle networks.
- Zededa - Zededa is a leading edge computing company that specializes in edge management and orchestration. Its platform enables secure management and orchestration of distributed edge nodes, facilitating IoT, AI, and 5G applications. With over $130 million in funding, Zededa is trusted by enterprises across sectors, including energy, manufacturing, and retail, to manage large-scale deployments with robust security and ease of use.
Risk Factors
- Cybersecurity Concerns - With data processed and stored closer to the edge, cybersecurity threats increase due to a larger attack surface. Edge devices are often less secure than centralized data centers, making them vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and malware. Managing security across decentralized networks is a challenge, especially in industries handling sensitive data like healthcare and finance.
- Interoperability Challenges - Edge computing involves diverse devices, platforms, and protocols from various manufacturers, leading to interoperability issues. Ensuring seamless communication across heterogeneous devices and networks can be costly and complex, requiring standardized frameworks and protocols to avoid data silos and integration problems.
- Regulatory Hurdles - With varying data privacy and security regulations across regions, companies implementing edge solutions must comply with laws like GDPR and HIPAA, which can be challenging when processing data across multiple jurisdictions. Non-compliance could lead to fines, reputational damage, and restrictions on edge deployments in regulated industries.
The Bottom Line
Edge computing presents exciting investment opportunities across various industries. While still emerging, it’s already showing how it can revolutionize data-driven operations in manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, and more. By enabling decentralized, real-time data processing, edge computing can tackle today’s biggest challenges in latency, security, and data management, making it a smart choice for forward-thinking investors.
At Acquinox, we are committed to identifying and evaluating breakthrough opportunities within these emerging fields. With our in-depth research, strategic insights, and extensive industry network, we empower our clients to navigate and capitalize on the most promising players and innovations in edge computing.
Published by Samuel Hieber

